D/D
1. Partial mole: triploidy
2. Twin gest one healthy and other complete mole
3. Placental mesenchymal dysplasia
4. Chorioangioma
Saturday, December 30, 2017
Partial mole withblive foetus
Tuesday, December 26, 2017
Biochemical genetics
GC/MS
Principle:
Separates components in a mixture (by GC) and do molecular analysis by mass spectroscopy (by MS)
mixture will separate into individual substances when heated. The heated gases are carried through a column with an inert gas (such as helium). As the separated substances emerge from the column opening, they flow into the MS. Mass spectrometry identifies compounds by the mass of the analyte molecule. A library of known mass spectra, covering several thousand compounds, is stored on a computer.
Wednesday, October 4, 2017
Foetal medicine
BPD- from 22 eka onwards
In maternal blood...Cmv igm..igg..Avidity
Friday, September 29, 2017
General
Funded by department of energy, united state s and national institute of health (NIH)
Budget sanctioned was 3 billion US dollar, and time scale of 15yrs was decided
Fragments are sequenced, and put together and assembled in chromosome.
Monday, September 25, 2017
Ataxia
1.Friedreich's ataxia
Symptoms begin sometime between the ages of 5 to 15 years
Progressive neurological degeneration
symptoms of poor coordination such as gait disturbance, scoliosis, heart disease and diabetes, but does not affect cognitive function
Genetics: gaa expansion in fxn gene
reduced expression of the mitochondrial protein frataxin
Tuesday, August 22, 2017
Growth and development
weight in infancy:
Head circumference
Development quotient
Maximum is 100. Calculated by dividing functional age with chronological age and multiplying by 100.
=/> 85 is normal
71-84 is mild to moderate delay
< /= 70 is severe delay
Sunday, July 30, 2017
Rett syndrome
affects girls exclusive ly
Normal development upto 6-18m
abnormal hand movt(washing, clapping etc.) slow growth, microcephaly, seizures, breathing problems, sleep disturbamces
gentics: IMECP2), X-Linked dominant, so males die in utero
case 161022 Spinocerebellar Ataxia type 1
2. bulbar function deterioration: Dysarthria
Saturday, July 29, 2017
Unexplained fractures in infancy:
Molecular genetics
structure of the primer should be simple and should not contain internal secondary structure to avoid internal folding.
primer-primer annealing which creates primer dimers and disrupts the amplification process, should be avoided
40-60% G/C content
Start and end with 1-2 G/C
pairsMelting temperature (Tm) of 50-60°C
Primer pairs should have a Tm within 5°C of each other
N is the number of nucleotide pairs in the primer ( primer length -1).
[Na+] is salt equivalent in mM.
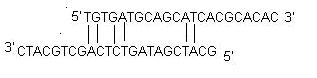
Tm of primer is the melting temperature of the less stable primer-template pair
Tm of product is the melting temperature of the PCR product.
first described in 1988 as a method to detect deletions in the dystrophingene
Multiplex-PCR consists of multiple primer sets within a single PCR mixture to produce amplicons of varying sizes that are specific to different DNA sequences
amplicon sizes, i.e., their base pair length, should be different enough to form distinct bands when visualized by gel electrophoresis. If amplicon size are same, primers are dyyed with different colour fluorescent dyes
1. Single template PCR reactions
2. Multiple template PCR reactions
1. Pathogen identification
2. SNP genotype
3. Gene Deletion Analysis
4. Mutation analysis
5. Linkage analysis
6. Forensic studies
Visual OMP
Primer plex
Notez
Sympt appear during ac illness
Mri..basal ganglia involved, bat wing appearance
Treatment....carnitine
+ Region in gene of longer than 500kb with no ORF are k/a desserts. 20% of human genome contains deserts.
+Human genome contains sequence that do not have coding function but still conserved through out species, this evolutionary conservation is certainly higher than the background level, which mandate them to be important.
+Repeated sequence accounts for more than 50% of genome, 45%of which are transposon
+Transposons are the sequence in genome that are mobile that is they are able to transport themselves to other region in genome.
Monday, May 29, 2017
compound hetrozygous
simple rule of thumb: in non-consanguineous parents , the most likely explanation for a recessive disease in offspring is compound heterozygosity for two different pathogenic mutations. Exceptions from this rule of thumb may be founder mutations in certain populations and specific gain of function mutations in certain genes such as e.g. FGFR2.
Tuesday, April 11, 2017
still birth
By defination Intrauterine foetal death (Stillbirth) is any foetal loss at 20 or more weeks of gestation.
Risk factors:
Maternal Thrombophillias:
a) Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome: characterised by presence of antiphospholipid antibodies, thrombosis and obstetrical complications, exact cause is uncertain but placental infalammation, thrombosis and decidual vasculopathy maay be involved.
b)Heritable Thrombophilias: that involves deficiency of anticoagulant protein or an increase in procoagulent protein. commonly associated with factor V Leiden mutation (FVL), prothrombin gene mutation, deficiency of anticoagulent proteins that are Protein C, S and Antithrombin III. various studies have shown poor associatin with stllbirth hence routine throm bophillia testing after stillbirth is not recommended.
thrombophillic defects may play a significant role in pacental abruption or infarction.
Infection: CMV is the most common congenirtally acquired infection during pregnancy.It can cause foetal and placental damage but its role in stillbirth is not clear.
infections with proven role are:
Bacterial pathogens: E. Colli, Group B Streptococci, Ureaplasm Urealyticum, Mycoplasm Hominis, Bacteroides species, Gardnerella, Mobilincus species and various enterococci.syphillis,
viral infections like Parvovirus B19 and enterovirus group.
Spirochetal disease: Syphillis, leptospirosis and lyme disease.
Foetal factors:
1. red cell alloimmunization:anti RhD, Anti Rhc and anti kell are most important in this respect.
2. platelet alloimmunization: result of maternal alloimmunization against fetal platelet antigens inherited from father.severe alloimmunization can cause intracranial hemorrhage and death.
3.chromosomal abnormality: overall fetal cytogenetic sbnormalities accounts for 6% to 10% of foetal loss, proportion is higher in malformed or macerated fetus.The distribution of chromosomal abnormality associated with stillbirths are as follows: trisomy21 31%, Monosomy X 22%, Trisomy18-22%, Trisomy 13- 6%and other chromosomal anomalies-19%
4. fetal single gene and mendelian disorders may also result in stillborn.common associations are:
Inborn errors of metabolism: Smith-Lemli-optiz Syndrome, Glycogen storage disease, peroxismal disorders and amino acid disorders
X-linked dominant mutations: lethal in male fetus due to skewed X-inactivation
autosomal dominent disorders: long QT interval, skeletal dysplasia
5. fetal structural anomalies: 25% of still
maternal : age less than 15 and more than 35 years, lowest risk is between 30-34 years, Obesity, gestational diabetes, hypertension, smoking, alcohol use, illicit drug use, Hypothyroidism, presence of TPO antibodies, Systemic Lupus arythromatosis, Intrahepatic chelestasis of pregnancy, inadequate prenatal care,
Obsterical profile: previous history of still birth or recurrent pregnancy loss,
Foetal factors: multiple gestation, IUGR
demographic factors: race and ethnicity
Causes:
Monday, March 27, 2017
QT interval
Large U waves (> 1mm) that are fused to the T wave should be included
improves detection of patients at increased risk of arrhythmias.
prolonged QTc
Wednesday, March 22, 2017
D/D
1. Hurler syndrome
2. MLC
3. Cardio-facio-cutaneous syndrome
d/d FLOPPY INFANT
1. Down syndrome
2. Zellweger syndrome, look like down syndrome
3. Prader Willi synd: feeding problem
4. Congenital myotonic dystrophy: extremely floppy, need ventilatory support at birth
D/D Rhizomelic shortening of bones
Tuesday, February 28, 2017
The telomere syndromes
fusion
cancer, was the first human disease in which telomeres were thought tohave a role. Telomerase activity was found to be upregulated in most cancers7
lung disease
premature-ageing syndromes
childhood onset:
Dyskeratosis congenita syndrome: dyskeratosis congenita 1 (DKC1) gene, encodes a conserved protein called dyskerin, it was as an essential component of the telomerase enzyme. skin hyperpigmentation, oral leukoplakia and nail dystrophy
Hoyeraal–Hreidarsson syndrome is characterized by developmental delay, immunodeficiency and cerebellar
hypoplasia.
Revesz syndrome is characterized by bilateral exudative retinopathy
Adult-onset manifestations of telomere-mediated disease:
more common due to germline TERT or TR loss-of-function mutations. Example: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). most common manifestation of telomere-mediated disease